- Visibility 71 Views
- Downloads 9 Downloads
- DOI 10.18231/j.ijcap.2020.068
-
CrossMark
- Citation
Study of anatomical variations of mental foramen in dry adult human mandibles and its clinical importance in Karnataka population
- Author Details:
-
Humaira Zainab
-
Sarita Sylvia *
-
Mohammed Khaleel Ahmed
Introduction
Mental foramen is a small foramen situated in anterolateral aspect of the body of the mandible. Normally, mental foramen is located below the interval between the premolars. It transmits mental nerve, artery and vein.[1], [2], [3], [4], [5], [6], [7], [8] Mental nerve is a branch of inferior alveolar nerve which supplies sensation to lower lip and the labial mucosa and lower canines and premolars. The most useful injection for anaesthetising the mandibular teeth is the inferior alveolar nerve block.[9], [10], [11], [12], [13], [14], [15] To anaesthetise the anterior teeth, including the premolars and canines, it is possible to avoid giving inferior alveolar nerve block by injecting anaesthetic solution adjacent to the mental foramen.[15], [16], [17], [18] So, the study of position and morphological variation of mental foramen is very important because it will be helpful to localise the important neurovascular bundle passing through the mental foramen.
Any foramen in addition to mental foramen in the body of the mandible is known as accessory mental foramen. Accessory mental foramen transmits the accessory branch of mental nerve. So, the knowledge of its position and incidence is helpful to dental surgeons to achieve complete anaesthesia because if this nerve is not blocked, anaesthesia will be incomplete. This knowledge will also helpful to prevent accessory nerve injury during periapical surgery.
Materials and Methods
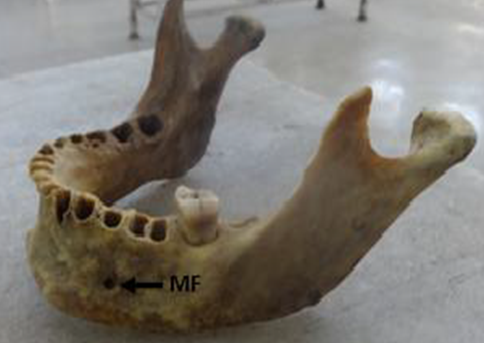
Present study included 120 dried adult human mandibles of both sexes obtained from Bone Bank of the Department of Anatomy. Bones which had deformities, damage, asymmetries, external pathological changes and fractures were excluded from the present study.
Campass asthesio meter was used to measure distance, shape, location on both sides of mandibles.
Location of mental foramen was identified by using following parameters.
Distance from mental foramen to mental symphysis.
Distance between the mental foramen to posterior border or ramus.
Distance from mental foramen to alveolar crest.
Distance from mental foramen to base of mental foramen.
Statistical analysis
The obtained data was analysed using descriptive statistics.
Results
The mean distance between the mental foramen and symphysis menti for right side was 23.21 mm±2.12 and for left side was 23.10 mm±2.41. The mean distance between mental foramen and posterior border of ramus of mandible for right side was 62.58 mm±4.23 and for left side was 63.84 mm±4.72 in [Table 1].
|
Landmarks |
Mean distances on right side(mm) |
Mean distances on left side(mm) |
|
Symphysis menti |
23.21±2.12 |
24.01±2.41 |
|
Posterior border of ramus of mandible |
62.58±4.23 |
63.84±4.72 |
|
Alveolar crest |
15.23±1.12 |
16.07±1.01 |
|
Base of mandible |
15.61± 1.03 |
15.98± 1.06 |
The mean distance between mental foramen and alveolar crest for right side was 15.23 mm±1.12 and for left side was 16.07 mm±1.01. The mean distance between the mental foramen and base of mandible for right side was 15.61 mm±1.03 and for left side was 15.98 mm±1.06.
|
Shape |
Study results |
|
Oval |
73.32% |
|
Round |
32.02% |
Shape of the mental foramen is oval 73.32% and round in 32.02% and in [Table 2].
|
Size (Mean diameter) |
Prabodha et al [14] |
Present study |
|
In oval shape |
2.97 mm |
2.37 mm |
|
In round shape |
2.11 mm |
2.02 mm |
The Mental foramen were mean diameter was 2.37 mm in oval shape and mean diameter was 2.02 mm in round shape in [Table 3].
|
Shape |
Prabodha et al[14] |
Priya et al[15] |
Present study |
|
Oval |
66.67% |
53.3% |
76.02%, |
|
Round |
33.33% |
34.67% |
76.33% |
|
Landmarks |
Prabodha et al [14] mm |
Sumit et al [19] mm |
Present study mm |
|
Symphysis menti |
26.52 |
29.12 |
23.21±2.12 |
|
Posterior border of ramus of mandible |
65.38 |
76.16 |
62.58±4.23 |
|
Alveolar crest |
12.15 |
14.45 |
15.23±1.12 |
|
Base of mandible |
13.3 |
13.85 |
15.61± 1.03 |
Discussion
The results of our study about position, shape and size were compared with that of other authors. In our study, the mean distance between the mental foramen and symphysis menti for right side was 23.21 mm±2.12 and for left side was 23.10 mm±2.41. The mean distance between mental foramen and posterior border of ramus of mandible for right side was 62.58 mm±4.23 and for left side was 63.84 mm±4.72. The mean distance between mental foramen and alveolar crest for right side was 15.23 mm±1.12 and for left side was 16.07 mm±1.01. The mean distance between the mental foramen and base of mandible for right side was 15.61 mm±1.03 and for left side was 15.98 mm±1.06. In 120 adult, dry mandibles studied by Sumit et al the mean distance of mental foramens was measure from symphysis menti, lower border of the body of the mandible and posterior border of the ramus of the mandible was 29.12mm, 14.45mm and 76.16mm. The common position for the mental foramen was in line with longitudinal axis of the lower second premolar was (75.8%), a position between first and second premolar were (12.2%) and followed by position in line with first molar was (3.33%). Accessory mental foramen was present in 8 mandibles (6.6%).[19]
Shape of the mental foramen is oval in 73.32% and round 32.02%. Deepa et al study shows that the shape of mental foramen was oval in 61.2% and rounded in 38.5% of mandibles in most of the studies. Accessory mental foramen was seen in 2 mandibles on right side (5.71%). Double mental foramen was present in 1 mandible (2%). The mean measurement of angle of the mandible was 128°.[20]
In 80 dry mandibles Lobes et al found that the mean distance of mental foramen measurement from symphysis menti and lower border of the body of the mandible was 26.14 mm and 13.83 mm respectively. The most common location of the mental foramen is in position with second premolar followed by the position between the first mandibular premolar and second premolar teeth.[21]
Ilayperuma et al studied 51 adult dry mandibles found that the mean distance of mental foramen from symphysis menti was 24.86 mm. The common position for the mental foramen was in line with longitudinal axis of the lower second premolar (52.94%) followed by a position between first and second premolar (26.47%). In many mandibles, the shape of the mental foramen was oval (59%). Multiple mental foramens were 3.92%.[22]
Deepa et al studied 100 dry mandibles and they found the mean distance of mental foramen measurement from symphysis menti and lower border of the body of the mandible was found 25.28 mm and 12.13 mm respectively. The common position for the mental foramen was in line with longitudinal axis of the lower second premolar in (81.52%) and position between first and second premolar was (7.7%) and followed by position in line with first molar was (7.9%). Double mental foramen was found in 2.6% of cases. The shape of mental foramen was oval in 92% and rounded in 8% of mandibles.[20]
Prabodha et al, studied 24 adult dry mandibles quoted that the mean distance of mental foramen measurement from symphysis menti, lower border of the body of the mandible and posterior border of the ramus of the mandible was 26.52 mm, 12.25 mm and 65.38 mm. As for as shape of mental foramen is concerned it was found oval in 66.67% and rounded in 33.33% of mandibles. Accessory mental foramen was also found in 2 mandibles (8.33%).[23] A Priya et al study 75 adult dry mandibles and found that the mean distance of mental foramens measurement from symphysis menti was 26.50mm respectively. The commonest position for the mental foramen was in line with longitudinal axis of the lower second premolar was (52%) and second premolar (23.33%). The shape of thel foramen was oval in 53.3% and rounded in 34.67% of mandibles. The opening of mental foramen was posterosuperiorly in 90.67% of mandibles.[24]
Conclusion
The present study of the mental foramen and the incidence of accessory mental foramen will provide helpful information to the oral and maxillofacial surgeon, oncosurgeon for performing procedure on the mandible. Which prevents complications, misinterpretations. also helps to plan and develop newer techniques for nerve blocks for surgery on mandible.
Therefore, identification of mental foramen in its various positions and its morphometric analysis is important for dental surgeons in nerve block and surgical procedures like apical curettage of mandibular premolars and periodontal surgery, to avoid injury to neurovascular bundle. In a majority of mandibles, we have found oval-shaped foramina lying in position IV. However, variations do exist in the position, shape, and size of mental foramen in different population groups. It is essential to be aware of the possibility of these anatomical variations while planning surgery in that region to avoid nerve damage and also to enable effective mental nerve block anaesthesia.
Source of Funding
None.
Conflict of Interest
None.
References
- R Singh, A K Srivastava. Study of position, shape, size and incidence of mental foramen and accessory mental foramen in Indian adult human skulls. Int J Morphol 2010. [Google Scholar]
- D R Agarwal, S B Gupta. Morphometric analysis of mental foramen in human mandibles of south Gujarat. People’s. J Sci Res 2011. [Google Scholar]
- W E Shankland. The position of mental foramen: in Asian Indians. J Oral Implantol 1994. [Google Scholar]
- D R Sawyer, M L Kiely, M A Pyle. The frequency of accessory mental foramina in four ethnic groups. Arch Oral Biol 1998. [Google Scholar]
- G Hauser, G F De Stefano. . Epigenetic variants of human skull 1989. [Google Scholar]
- L B Çağirankaya, H Kansu. An Accessory Mental Foramen: A Case Report. J Contemp Dent Pract 2008. [Google Scholar]
- R Rakhi, B Virendra, D K Sathpathi, S Sandeep, G K Kumar. Morphology and morphometry of the mental foramen in dry adult human mandibles from central India and their clinical correlation. Eur J Anat 2012. [Google Scholar]
- D K Sankar, P J Susan, S P Bhanu. Morphometrical and morphological study of mental foramen in dry dentulous mandibles of South Andhra population of India. Indian J Dent Res 2011. [Google Scholar]
- K Katakami, A Mishima, K Shiozaki, S Shimoda, Y Hamada, K Kobayashi. Characteristics of Accessory Mental Foramina Observed on Limited Cone-beam Computed Tomography Images. J Endod 2008. [Google Scholar]
- A Boronatlópez, M Peñarrochadiago. Failure of locoregionalanesthesia in dental practice: review of the literature. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal 2006. [Google Scholar]
- T Hanihara, H Ishida. Frequency variations of discrete cranial traits in major human populations. IV. Vessel and nerve related variations. J Anat 2001. [Google Scholar]
- A H R Rowe. . Clinical Dentistry 1986. [Google Scholar]
- M S Chung, H J Kim, H S Kang, I H Chung. Locational relationship of the supraorbital notch or foramen and infraorbital and mental foramina in Koreans. Acta Anat 1995. [Google Scholar]
- W Apinhasmit, D Methathrathip, S Chompoopong, S Sangvichien. Mental foramen in Thais: an anatomical variation related to gender and side. Surg Radiol Anat 2006. [Google Scholar]
- S Agthong, T Huanmanop, V Chentanez. Anatomical Variations of the Supraorbital, Infraorbital, and Mental Foramina Related to Gender and Side. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2005. [Google Scholar]
- H Yesilyurt, A Aydinilioglu, A Kavakli, N Ekinci, C Eroglu, M Hacialiogullari. Local differences in the position of the mental foramen. Folia Morphol 2008. [Google Scholar]
- A Chandra, A Singh, M Badni, R Jaiswal, A Agnihotri. Determination of sex by radiographic analysis of mental foramen in North Indian population. J Forensic Dent Sci 2013. [Google Scholar]
- T M Wang, C Shih, J C Liu, K J Kuo. A clinical and anatomical study of the location of the mental foramen in adult Chinese mandibles. Acta Anat 1986. [Google Scholar]
- G Sumit, S S Jagdish. Study of anatomical variations and incidence of mental foramen and accessory mental foramen in dry human mandibles. Natl J Med Res 2012. [Google Scholar]
- R A Deepa, B G Sandeep. Morphometric analysis of mental foramen in human mandibles of South Gujarat. People’s J Sci Res 2011. [Google Scholar]
- P T C Lopes, G A M Pereira, A M P V Santos. Location of the mental foramen in dry mandibles of adult individuals in Southern Brazil. J Morphol Sci 2010. [Google Scholar]
- I Ilayperuma, G Nanayakkara, N Palahepitiya. Morphometric Analysis of the Mental Foramen in Adult Sri Lankan Mandibles. Int J Morphol 2009. [Google Scholar]
- L B L Prabodha, B G Nanayakkara. The position, dimensions and morphological variations of mental foamen in mandibles. Galle Med J 2006. [Google Scholar]
- P R Priya, M P Ambali, M A Doshi, S D Jadhav. Variation in the position and shape and direction of mental foramen in dry mandible. Int J Anat Res 2014. [Google Scholar]
